Parallelism and Parallel Properties
A data–flow enables task parallelism, inherently. Different units in a linear data–flow can run on different processes in a data–pipeline. The branches in a data–flow make total ordering of computation into partial ordering. The two branches can run in separate processes and their results can be merged later in the data–flow if needed. In practical MPI applications task parallelism is beneficial only if the computation on each process is intensive compared to the relatively higher communication costs of message passing.
The map and reduce enable data parallelism. A single map unit can be made to run on separate processes on different rows simultaneously. A reduce is parallel on different groups of rows, however it requires that all the rows in a group be communicated to the same processor from the map processes.
Configuring parallelism in easyLambda involves modifying the process allocation and data distribution behaviours either for a unit or the dataflow itself. The section, first presents the defaults for parallelism chosen in easyLambda and then shows how it can be customized with properties that are common across the units.
Process Allocation Defaults
By default, all the processes available to the MPI environment are also available to the dataflow. The run or get expressions have optional parameters for process requests that limits the processes allocated to the dataflow. Process allocation can be requested by specifying a process count either as an integer or as a ratio of total processes used by its source unit. Specific processes can also be requested by specifying their MPI ranks.
The rise unit runs on all the processes available to the dataflow. The map and filter units run on the same processes as their source units and receive data via function calls from them.
The key partitioning reduce, reduceAll and zip run in parallel on half the number of processes that their sources have. These units without key partitioning run on a single process as all the rows need to be present in a single process to be reduced or joined.
Data Distribution Defaults
If map or filter units are configured to run in parallel without specifying the keys for partitioning, the default data distribution behaviour is to share the input data rows among the processes in a round-robin fashion.
If partition by key is specified for a unit, the hash function is used to partition the data across the processes. These defaults can be overridden.
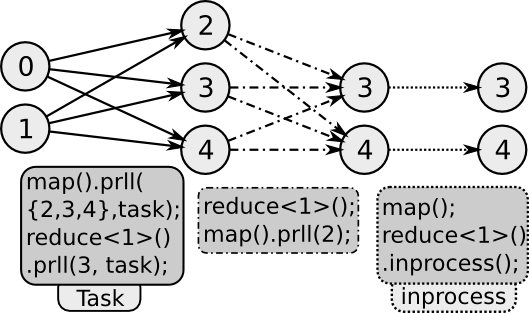
Check demoPrll for usage. The following are the properties that can be added to any unit to change its parallel behaviour.
Prll Property
The prll property configures process allocation and data distribution semantics for a unit. Process allocation can be requested by specifying a process count either as an integer or as a ratio of processes used by the source/parent unit. Specific processes can also be requested by specifying their MPI ranks. If the request cannot be satisfied, the program still executes with the closest possible allocation.
As an example the prll property can be used with one process or by specifying the exact rank of the process that needs to collect all the output streaming rows. The get expression can be used in combination with this to use the output data outside the dataflow.
The prll property takes process request as first parameter. The second optional parameter modifies the default modes of data distribution and allocation for that unit. The task mode allots processes from those available to the dataflow rather than from its source or parent unit. Without using task mode, a unit cannot run on any other process outside the set of processes available to its source/parent. Task mode can be used in combination with the data distribution modes shard or dupe. If shard mode is specified, rows are distributed amongst the processes in a round–robin fashion. This mode is effective only if the data partitioning is not specified for the unit. If dupe mode is specified, the rows are duplicated and made available to all the processes.
The dupe mode can be used to replicate the functionality of the broadcast function in MPI. This can be used to communicate the results at a certain step in the computation or the result rows using get() available to all the processes. this data can then be used outside easyLambda as well.
Inprocess property
The inprocess property removes all parallelism behaviour from the unit. The unit runs on the same set of processes as its source and there is no data distribution across processes. The map and filter operations run in–process by default. reduce and other units can be configured to run in-process using the inprocess property. In-process reduction is a frequently used pattern in parallel programming and is sometimes termed as a Combiner operation. The advantage of an in–process reduction prior to a global reduction is that only single locally reduced row needs to be communicated per key to find the global reduction. This reduces communication overhead.
PartitionBy property
The partitionBy property can be used to configure the columns and function to be used for partitioning. The key columns in reduce, reduceAll, scan and zip are also used for partitioning between processes. However the partitioning columns need to be specified explicitly for a map or filter operation. The partitionBy property takes key columns as template arguments for map and filter. It takes an optional argument to customize the partitioning function.